CATEGORIES
FEATURED PRODUCTS
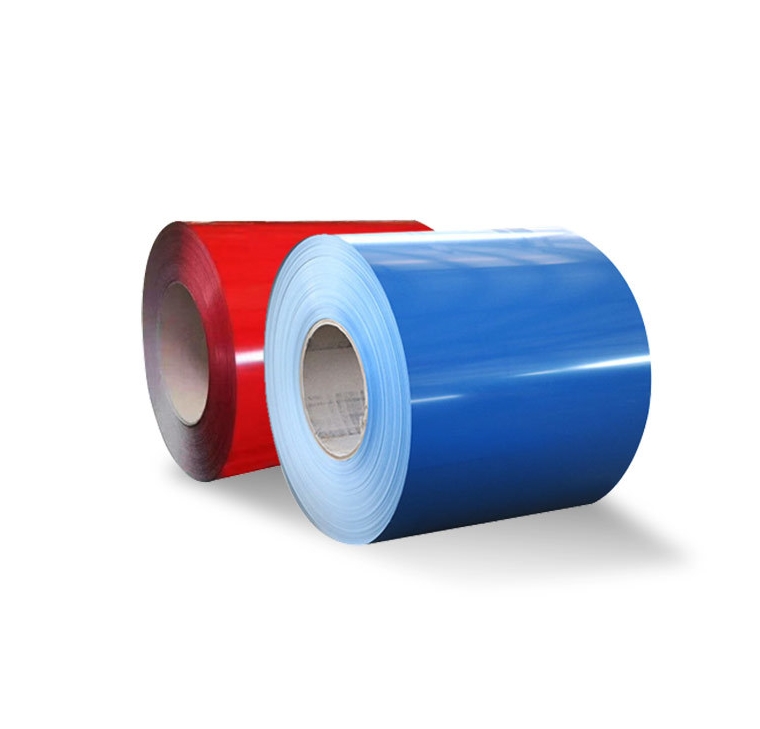
ASTM A240 410 stainless steel coil
We offer this product and related grades with 100% factory direct pricing and free quotes available within 24 hours.
APPLICATION SCENARIOS

OUR ADVANTAGE
Certificate of Honor
PARTNER

Our Factory

410 stainless steel coil represents one of the most versatile martensitic stainless steel grades in today’s manufacturing landscape. What makes this material unique? With 11.5% to 13.5% chromium and no nickel, it emphasizes strength and hardness over corrosion resistance compared to austenitic grades. We manufacture this grade to meet stringent industry standards while maintaining cost-effectiveness.
The martensitic structure provides excellent mechanical properties through heat treatment. Unlike austenitic stainless steels, 410 grade can be hardened and tempered to achieve specific strength requirements. This characteristic makes it particularly valuable for applications requiring wear resistance and high tensile strength.
Our production capabilities ensure consistent quality across various coil dimensions. The material demonstrates magnetic properties in both annealed and hardened conditions, distinguishing it from many other stainless steel grades.
Chemical Composition and Properties
Chemical Composition Table
| Element | Weight % | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | 0.08-0.15 | Hardness enhancement |
| Chromium (Cr) | 11.5-13.5 | Corrosion resistance |
| Manganese (Mn) | 1.00 max | Deoxidizing agent |
| Phosphorus (P) | 0.040 max | Impurity control |
| Sulfur (S) | 0.030 max | Machinability |
| Silicon (Si) | 1.00 max | Strength improvement |
| Nickel (Ni) | 0.75 max | Limited content |
Mechanical Properties
The mechanical characteristics of 410 stainless steel coil vary significantly based on heat treatment conditions:
| Property | Annealed | Hardened & Tempered |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 485-620 MPa | 690-1035 MPa |
| Yield Strength | 275-415 MPa | 515-860 MPa |
| Elongation | 20-25% | 15-20% |
| Hardness | 85-95 HRB | 40-54 HRC |
| Impact Strength | 68-75 J | 27-41 J |
Physical Properties
Understanding physical properties helps in processing and application design:
- Density: 7.70 g/cm³
- Melting Point: 1480-1530°C
- Thermal Conductivity: 24.9 W/m·K at 100°C
- Electrical Resistivity: 0.57 μΩ·m
- Magnetic Properties: Ferromagnetic
Manufacturing Process and Quality Control
We employ advanced manufacturing techniques to produce high-quality 410 stainless steel coil. The process begins with electric arc furnace melting, followed by secondary refining to achieve precise chemical composition. Continuous casting creates the initial billet form.
Hot rolling reduces thickness while maintaining material integrity. Cold rolling then achieves final dimensions and surface finish. Throughout production, we implement rigorous quality control measures including chemical analysis, mechanical testing, and dimensional verification.
Heat treatment capabilities allow us to deliver material in various conditions. Annealing provides maximum ductility for forming operations. Hardening and tempering achieve specific strength requirements for end-use applications.
Surface treatments enhance both appearance and performance. Mill finish provides the standard surface condition, while additional treatments can achieve specific roughness or appearance requirements.
Technical Specifications and Standards
International Standards Compliance
| Standard | Designation | Scope |
|---|---|---|
| ASTM A240 | 410 | Pressure vessels |
| ASTM A276 | 410 | Bars and shapes |
| AISI/SAE | 410 | General classification |
| UNS | S41000 | Unified numbering |
| EN | 1.4006 | European standard |
| JIS | SUS410 | Japanese standard |
Available Dimensions
We stock and manufacture 410 stainless steel coil in various specifications:
Thickness Range: 0.3mm to 6.0mm Width Range: 100mm to 1500mm Coil Weight: Up to 25 tons Surface Finish: 2B, BA, No.1, No.4
Tolerance Standards
Dimensional tolerances meet international standards:
- Thickness: ±0.05mm for material under 3mm
- Width: ±3mm for standard widths
- Edge Condition: Mill edge or slit edge available
Applications Across Industries
Automotive Industry
The automotive sector represents a significant market for 410 stainless steel coil. Exhaust system components benefit from the material’s high-temperature strength and moderate corrosion resistance. Valve components utilize the hardening capability for wear resistance.
Fastener applications leverage the magnetic properties and strength characteristics. Trim components take advantage of the material’s formability in the annealed condition and subsequent hardening potential.
Cutlery and Kitchenware
Food service applications capitalize on the material’s ability to take a high polish and maintain sharp edges. Knife blades demonstrate excellent edge retention after proper heat treatment. Kitchen utensils benefit from the combination of strength and moderate corrosion resistance.
Industrial cutting tools utilize the wear resistance characteristics. Surgical instruments require the precise hardness control possible with this grade.
Industrial Applications
Pump components operate effectively in mildly corrosive environments. Valve trim applications benefit from the erosion resistance. Fastener applications span multiple industries due to the strength and magnetic properties.
Heat exchanger components function well in specific temperature ranges. Screening equipment utilizes the wear resistance characteristics for extended service life.
Comparison with Other Stainless Steel Grades
410 vs 304 Stainless Steel
| Property | 410 | 304 |
|---|---|---|
| Chromium Content | 11.5-13.5% | 18-20% |
| Nickel Content | 0.75% max | 8-10.5% |
| Magnetic Properties | Magnetic | Non-magnetic |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Hardness Potential | High | Low |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
410 vs 420 Stainless Steel
Both grades share similar chromium content, but 420 contains higher carbon levels. This difference affects hardness potential and corrosion resistance. 420 achieves higher hardness but sacrifices some corrosion resistance compared to 410.
410 vs 416 Stainless Steel
416 grade contains added sulfur for improved machinability. This modification enhances cutting characteristics but reduces corrosion resistance. 410 provides better corrosion resistance while 416 offers superior machining properties.
Heat Treatment and Processing Guidelines
Annealing Process
Full annealing requires heating to 815-900°C followed by furnace cooling. This treatment produces maximum ductility and lowest hardness for forming operations. Stress relief annealing at 650-750°C removes residual stresses without full softening.
Hardening Procedures
Hardening involves heating to 925-1010°C followed by air or oil quenching. The cooling rate affects final hardness and should be selected based on section thickness and desired properties.
Tempering Operations
Tempering reduces brittleness while maintaining strength. Temperature ranges from 150-650°C depending on required hardness levels. Lower temperatures maintain maximum hardness while higher temperatures improve toughness.
Welding Considerations
Welding 410 stainless steel requires preheating to 200-300°C for thick sections. Post-weld heat treatment ensures optimal properties in the heat-affected zone. Matching filler metals maintain corrosion resistance and mechanical properties.
Corrosion Resistance and Environmental Performance
410 stainless steel demonstrates good corrosion resistance in mild environments. The chromium content provides protection against atmospheric corrosion and many organic acids. However, performance limitations exist in chloride environments and highly oxidizing conditions.
Pitting resistance depends on surface finish and environmental conditions. Smooth surfaces perform better than rough finishes. Regular maintenance extends service life in challenging environments.
Temperature affects corrosion behavior. Elevated temperatures can reduce resistance in some environments while improving performance in others. Understanding these relationships helps optimize material selection.
Galvanic corrosion can occur when 410 is coupled with more noble metals. Proper design considerations minimize this risk through material selection and protective measures.
Market Trends and Industry Outlook
The global stainless steel market size was calculated at USD 127.07 billion in 2024 and is projected to hit around USD 241.70 billion by 2034 with a CAGR of 6.64%. This growth drives demand for specialized grades like 410 stainless steel coil.
The Stainless Steel Market size is expected to reach 13.40 million tons in 2025 and grow at a CAGR of 4.69% to reach 16.85 million tons by 2030. Martensitic grades represent a significant portion of this market due to their unique property combinations.
Automotive electrification creates new opportunities for 410 stainless steel applications. Battery housing components and structural elements benefit from the strength and formability characteristics.
Infrastructure development worldwide drives demand for corrosion-resistant materials. 410 stainless steel coil fits many applications where moderate corrosion resistance meets strength requirements.
Quality Assurance and Testing
Our quality management system ensures consistent product performance. Chemical analysis verifies composition compliance with specifications. Mechanical testing confirms strength and ductility requirements.
Non-destructive testing methods detect internal defects. Ultrasonic inspection identifies inclusions and laminations. Surface inspection ensures cosmetic quality standards.
Dimensional verification confirms thickness, width, and flatness specifications. Statistical process control maintains consistency across production runs.
Customer-specific testing accommodates unique requirements. Specialized testing capabilities support material qualification for critical applications.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
410 stainless steel offers excellent recyclability characteristics. The material can be recycled indefinitely without property degradation. This feature supports sustainable manufacturing practices and reduces environmental impact.
Energy efficiency in production continues improving through technological advances. Modern melting practices reduce energy consumption while maintaining quality standards.
Longevity in service applications reduces replacement frequency. This characteristic contributes to overall sustainability through reduced material consumption over product lifecycles.
Life cycle assessment studies demonstrate favorable environmental profiles compared to alternative materials in many applications.
Future Developments and Innovations
Advanced processing techniques promise improved properties and cost reduction. Powder metallurgy methods enable near-net-shape production for complex components. Additive manufacturing expands design possibilities for specialized applications.
Surface modification technologies enhance performance characteristics. Nitriding treatments improve wear resistance. Coating technologies extend corrosion resistance capabilities.
Alloy development continues refining composition for specific applications. Micro-alloying elements enhance particular properties while maintaining cost-effectiveness.
Digital technologies improve quality control and traceability. Real-time monitoring systems detect process variations before they affect product quality.
Specifications Table
| Parameter | Value/Range | Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | ||
| Carbon | 0.08-0.15% | ASTM A240 |
| Chromium | 11.5-13.5% | ASTM A240 |
| Manganese | 1.00% max | ASTM A240 |
| Mechanical Properties | ||
| Tensile Strength (Annealed) | 485-620 MPa | ASTM A240 |
| Yield Strength (Annealed) | 275-415 MPa | ASTM A240 |
| Elongation | 20-25% | ASTM A240 |
| Physical Properties | ||
| Density | 7.70 g/cm³ | Standard |
| Melting Point | 1480-1530°C | Standard |
| Dimensions | ||
| Thickness | 0.3-6.0mm | Custom |
| Width | 100-1500mm | Custom |
| Weight | Up to 25 tons | Custom |
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What applications are best suited for 410 stainless steel coil?
A: 410 stainless steel coil excels in applications requiring moderate corrosion resistance combined with high strength and hardness. Primary applications include cutlery, automotive components, fasteners, valve trim, and industrial equipment parts. The material’s ability to be hardened makes it ideal for wear-resistant applications.
Q: How does 410 stainless steel compare to 304 grade in terms of corrosion resistance?
A: 410 stainless steel provides moderate corrosion resistance suitable for mild environments, while 304 grade offers superior corrosion resistance in a broader range of conditions. The lower chromium content in 410 reduces its corrosion resistance but enables higher strength and hardness potential through heat treatment.
Q: Can 410 stainless steel coil be welded effectively?
A: Yes, 410 stainless steel can be welded using standard techniques with proper precautions. Preheating to 200-300°C is recommended for thick sections. Post-weld heat treatment ensures optimal properties in the heat-affected zone. Matching filler metals maintain corrosion resistance and mechanical properties.
Q: What heat treatment options are available for 410 stainless steel?
A: 410 stainless steel can be annealed for maximum ductility, hardened for maximum strength, or tempered for balanced properties. Annealing involves heating to 815-900°C followed by furnace cooling. Hardening requires heating to 925-1010°C with air or oil quenching. Tempering at 150-650°C adjusts hardness levels.
Q: Is 410 stainless steel magnetic?
A: Yes, 410 stainless steel exhibits ferromagnetic properties in both annealed and hardened conditions. This magnetic characteristic distinguishes it from austenitic stainless steels like 304 and 316 grades, making it suitable for applications requiring magnetic properties.
Q: What surface finishes are available for 410 stainless steel coil?
A: Standard surface finishes include 2B (smooth, reflective), BA (bright annealed), No.1 (hot rolled, pickled), and No.4 (brushed). Custom finishes can be achieved through additional processing. Surface finish affects both appearance and corrosion resistance performance.