In industrial applications, the pressure rating of stainless steel pipes is a critical factor in determining the pipe's capability to withstand internal pressures without failure. For SCH 40 stainless steel pipes, understanding the pressure rating is crucial for safe and efficient system design. As experts in the field of metal materials, we will break down the details of SCH 40 stainless steel pipes, their pressure rating, and how to choose the right pipe for your application.
What is SCH 40 Stainless Steel Pipes
SCH 40 is a standard schedule used to describe the wall thickness of pipes. Stainless steel pipes are commonly classified by their schedule number, with SCH 40 being one of the most widely used grades. The wall thickness of SCH 40 stainless steel pipes varies depending on the pipe's diameter, and it is essential to understand how this impacts the pressure rating.
Pressure Rating of SCH 40 Stainless Steel Pipe
The pressure rating of SCH 40 stainless steel pipes depends on several factors, including the pipe material, diameter, temperature, and wall thickness. For most standard conditions, SCH 40 stainless steel pipes can handle pressure ratings ranging from 150 to 800 psi (pounds per square inch) depending on the pipe diameter and the specific grade of stainless steel used.
Factors Affecting Pressure Rating
Several factors influence the pressure rating of a stainless steel pipe:
- Material Strength: Stainless steel grades such as 304 and 316 offer different pressure ratings due to their varied material properties.
- Temperature: The pressure rating will decrease as the temperature of the fluid within the pipe increases. High-temperature environments require pipes with higher pressure ratings.
- Pipe Diameter: Larger pipes will generally have a lower pressure rating compared to smaller pipes with the same wall thickness.
- Wall Thickness: A thicker pipe wall can handle higher pressures, which is why SCH 40 is considered a moderate-grade pipe thickness.
Pressure Rating for Different Stainless Steel Grades
Different stainless steel grades offer varying pressure ratings, even within the same SCH 40 schedule. For example:
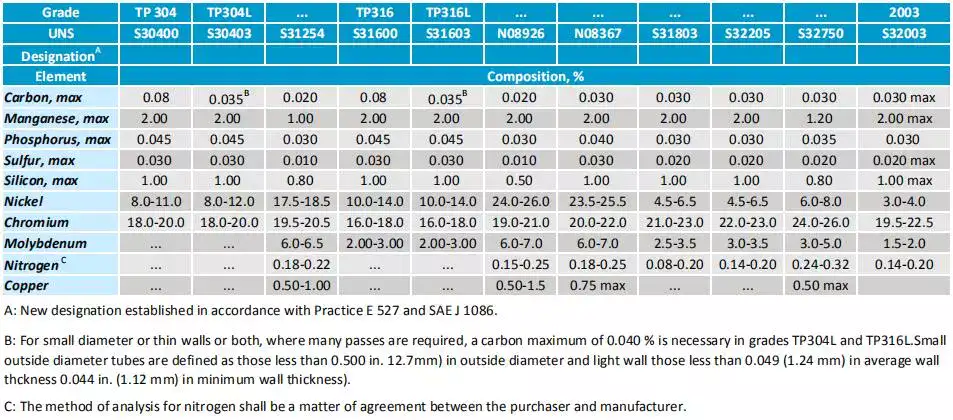
- 304 Stainless Steel: Known for its excellent corrosion resistance, SCH 40 304 stainless steel pipes are commonly used in a variety of industrial applications with pressure ratings of around 450 psi for 2-inch diameter pipes.
- 316 Stainless Steel: Offering superior resistance to corrosion, SCH 40 316 stainless steel pipes have a higher pressure rating compared to 304, typically around 600 psi for 2-inch diameter pipes.
Pressure Testing and Compliance
When selecting a SCH 40 stainless steel pipe, it is essential to ensure that it meets the required pressure testing standards. The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) provides specific guidelines for testing the pressure rating of stainless steel pipes, including hydrostatic pressure tests, which ensure the pipe can withstand the necessary pressure without failure.
Applications of SCH 40 Stainless Steel Pipes
SCH 40 stainless steel pipes are commonly used in a variety of industries due to their balance of strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness. Some of the common applications include:
- Water Systems: For potable water distribution and drainage.
- Oil and Gas: For transportation of liquids and gases at moderate pressure.
- Food and Beverage: For handling liquid food products due to corrosion resistance.
- Chemical Processing: To handle moderate pressures and corrosive substances.
Comparing SCH 40 to Other Schedules
When designing systems, comparing SCH 40 to other schedules, such as SCH 80 or SCH 160, is essential for selecting the right pipe. SCH 40 pipes are suitable for lower-pressure applications, while SCH 80 and SCH 160 pipes are used for higher-pressure environments due to their thicker walls.
| Pipe Schedule | Wall Thickness (inches) | Pressure Rating for 2" Pipe (psi) |
|---|---|---|
| SCH 40 | 0.154 | 450 |
| SCH 80 | 0.218 | 700 |
| SCH 160 | 0.375 | 1000 |
Choosing the Right SCH 40 Stainless Steel Pipe for Your Application
Selecting the right SCH 40 stainless steel pipe involves considering several factors, such as:
- The fluid type and its temperature.
- The pressure requirements of your system.
- The diameter of the pipe.
- Whether the pipe will be exposed to corrosive environments or extreme temperatures.
Installation Considerations
When installing SCH 40 stainless steel pipes, it is essential to ensure that the installation conditions match the pipe's pressure rating. Using compatible fittings and ensuring proper welding techniques will help maintain the pipe’s integrity under pressure.
Maintenance and Inspection
Regular maintenance and inspection are key to ensuring the longevity and performance of SCH 40 stainless steel pipes. Factors like corrosion, wear, and scaling can impact the pressure rating over time. Routine inspections should focus on identifying any signs of damage, such as cracks, leaks, or material fatigue.
Safety and Regulatory Standards
When selecting and installing SCH 40 stainless steel pipes, it is crucial to comply with local and international safety and regulatory standards. These standards ensure that the pipes are suitable for their intended applications and can safely withstand the pressures they will be exposed to.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the pressure rating for SCH 40 stainless steel pipes?
The pressure rating for SCH 40 stainless steel pipes typically ranges from 150 psi to 800 psi, depending on the pipe diameter and the material grade.
2. How does temperature affect the pressure rating of SCH 40 pipes?
As the temperature increases, the pressure rating decreases. It is important to account for temperature changes in high-temperature applications.
3. What is the difference between SCH 40 and SCH 80 stainless steel pipes?
SCH 80 pipes have thicker walls and higher pressure ratings than SCH 40 pipes, making them suitable for higher-pressure applications.
4. Can SCH 40 stainless steel pipes be used for gas pipelines?
Yes, SCH 40 stainless steel pipes are commonly used in gas pipelines, though higher-pressure systems may require SCH 80 or SCH 160 pipes.
5. What is the standard for testing the pressure rating of stainless steel pipes?
The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) provides specific testing standards, including hydrostatic pressure tests, to determine the pressure rating of stainless steel pipes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, SCH 40 stainless steel pipes offer a reliable and versatile solution for moderate pressure applications across various industries. By understanding the factors influencing the pressure rating, choosing the right material grade, and following proper installation practices, you can ensure optimal performance and safety.